Lower-Level Agent API#
We offer a lower-level agent API that offers a host of capabilities beyond simply executing a user query end-to-end.
These capabilities let you step through and control the agent in a much more granular fashion. The end goal is that you can create reliable agentic software systems over your data.
We took inspiration from the Agent Protocol, the OpenAI Assistants API, and of course a host of agent research papers.
NOTE: This is still under development, so interfaces may change. In fact, we’d love to get your feedback on how to make this better.
High-Level Agent Architecture#
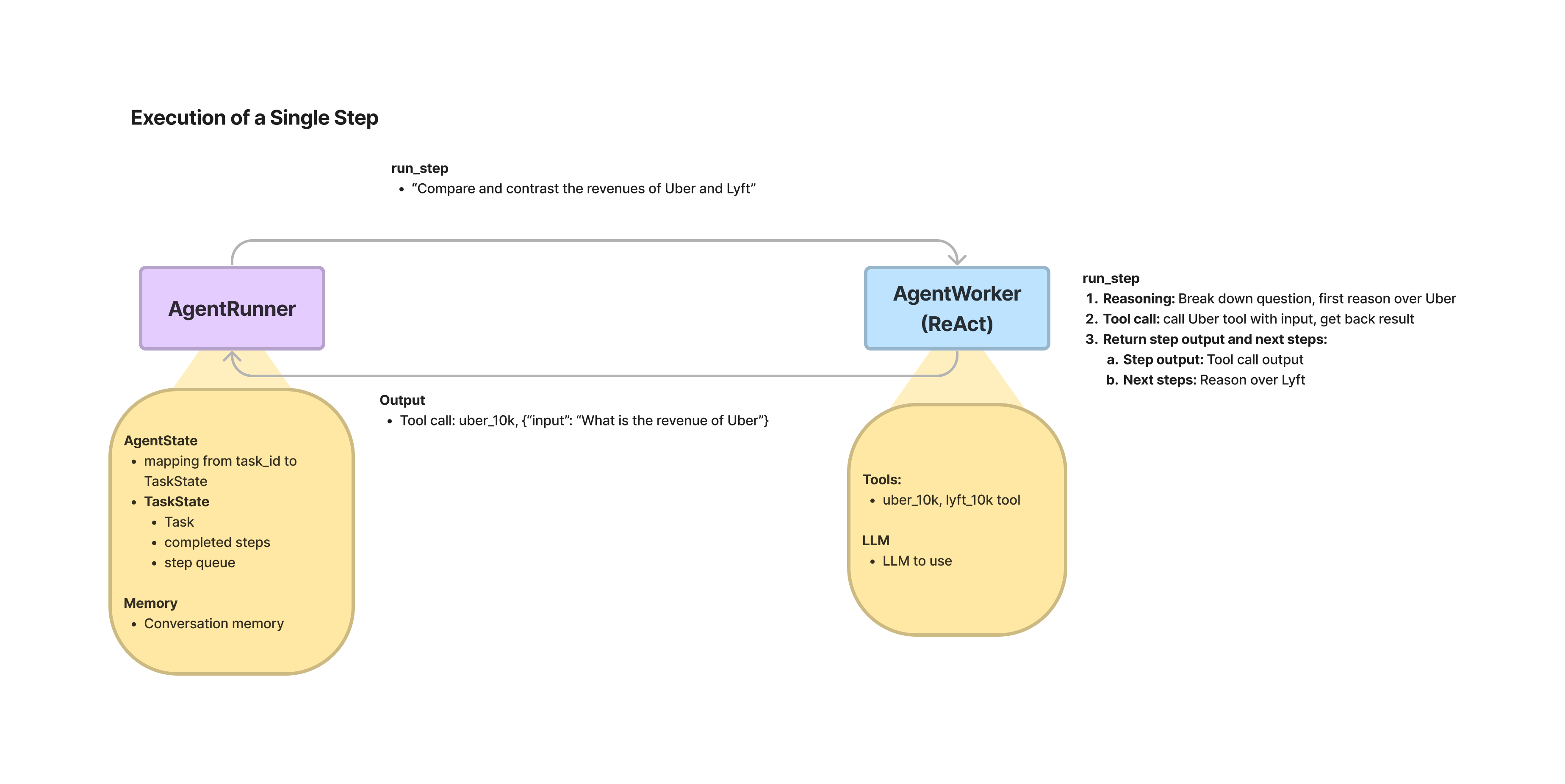
Our “agents” are composed of AgentRunner objects that interact with AgentWorkers:
AgentRunners are orchestrators that store state (including conversational memory), create and maintain tasks, run steps through each task, and offer the user-facing, high-level interface for users to interact with.AgentWorkers control the step-wise execution of a Task. Given an input step, an agent worker is responsible for generating the next step. They can be initialized with parameters and act upon state passed down from the Task/TaskStep objects, but do not inherently store state themselves. The outerAgentRunneris responsible for calling anAgentWorkerand collecting/aggregating the results.
Some auxiliary classes:
Task: high-level task, takes in a user query + passes along other info like memoryTaskStep: represents a single step. Feed this in as input toAgentWorker, get back aTaskStepOutput. Completing aTaskcan involve multipleTaskStep.TaskStepOutput: Output from a given step execution. Outputs whether or not a task is done.
Benefits#
Here are some key benefits to using this lower-level API:
Decouple task creation from execution - control when you want to execute a given task.
Get greater debuggability into the execution of each step.
Get greater visibility: view completed steps and next steps.
[Coming Soon] Steerability: directly control/modify intermediate steps by injecting human feedback
Abandon task: give up if a task has derailed throughout the course of execution, without affecting the core agent memory.
[Coming Soon] Undoing a step.
Easier Customization: it’s easy to subclass/implement new agent algorithms (incl. ReAct, OpenAI, but also plan+solve, LLMCompiler) by implementing an
AgentWorker.
Usage Pattern#
You can either use an OpenAIAgent or ReActAgent, or create your own via the AgentRunner and AgentWorker:
from llama_index.agent import AgentRunner, OpenAIAgentWorker
# construct OpenAIAgent from tools
openai_step_engine = OpenAIAgentWorker.from_tools(tools, llm=llm, verbose=True)
agent = AgentRunner(openai_step_engine)
# create task
task = agent.create_task("What is (121 * 3) + 42?")
# execute step
step_output = agent.run_step(task)
# if step_output is done, finalize response
if step_output.is_last:
response = agent.finalize_response(task.task_id)
# list tasks
task.list_tasks()
# get completed steps
task.get_completed_steps(task.task_id)
print(str(response))
NOTE: The older legacy implementations of OpenAIAgent and ReActAgent (which did not allow for step-wise execution) are still available via:
from llama_index.agent import OldOpenAIAgent, OldReActAgent
Additional Module Guides#
Check out our lower-level agent module guides for more details!