Advanced Multi-Modal Retrieval using GPT4V and Multi-Modal Index/Retriever#
In this notebook, we show how to build a Multi-Modal retrieval system using LlamaIndex with GPT4-V and CLIP.
LlamaIndex Multi-Modal Retrieval
Text embedding index: Generate GPT text embeddings
Images embedding index: CLIP embeddings from OpenAI for images
Encoding queries:
Encode query text for text index using ada
Encode query text for image index using CLIP
Framework: LlamaIndex
Steps:
Using Multi-Modal LLM GPT4V class to undertand multiple images
Download texts, images, pdf raw files from related Wikipedia articles and SEC 10K report
Build Multi-Modal index and vetor store for both texts and images
Retrieve relevant text and image simultaneously using Multi-Modal Retriver according to the image reasoning from Step 1
%pip install llama_index ftfy regex tqdm
%pip install git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git
%pip install torch torchvision
%pip install matplotlib scikit-image
%pip install -U qdrant_client
import os
OPENAI_API_TOKEN = ""
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = OPENAI_API_TOKEN
Download images from Tesla website for GPT4V image reasoning#
from pathlib import Path
input_image_path = Path("input_images")
if not input_image_path.exists():
Path.mkdir(input_image_path)
!wget "https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1nUhsBRiSWxcVQv8t8Cvvro8HJZ88LCzj" -O ./input_images/long_range_spec.png
!wget "https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=19pLwx0nVqsop7lo0ubUSYTzQfMtKJJtJ" -O ./input_images/model_y.png
!wget "https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1utu3iD9XEgR5Sb7PrbtMf1qw8T1WdNmF" -O ./input_images/performance_spec.png
!wget "https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1dpUakWMqaXR4Jjn1kHuZfB0pAXvjn2-i" -O ./input_images/price.png
!wget "https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1qNeT201QAesnAP5va1ty0Ky5Q_jKkguV" -O ./input_images/real_wheel_spec.png
Generate image reasoning from GPT4V Multi-Modal LLM#
Plot input images#
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
image_paths = []
for img_path in os.listdir("./input_images"):
image_paths.append(str(os.path.join("./input_images", img_path)))
def plot_images(image_paths):
images_shown = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 9))
for img_path in image_paths:
if os.path.isfile(img_path):
image = Image.open(img_path)
plt.subplot(2, 3, images_shown + 1)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
images_shown += 1
if images_shown >= 9:
break
plot_images(image_paths)
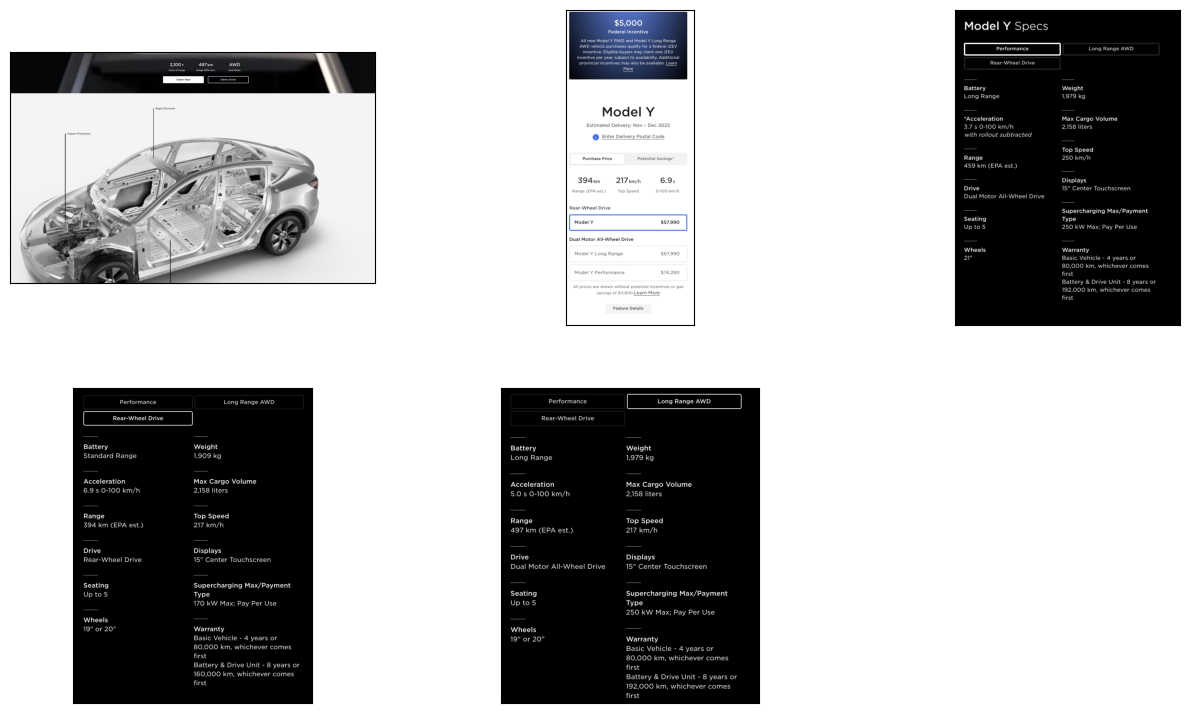
Using GPT4V to understand those input images#
from llama_index.multi_modal_llms.openai import OpenAIMultiModal
from llama_index import SimpleDirectoryReader
# put your local directore here
image_documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./input_images").load_data()
openai_mm_llm = OpenAIMultiModal(
model="gpt-4-vision-preview", api_key=OPENAI_API_TOKEN, max_new_tokens=1500
)
response_1 = openai_mm_llm.complete(
prompt="Describe the images as an alternative text",
image_documents=image_documents,
)
print(response_1)
The images depict information and specifications about electric vehicles, presumably from a car manufacturer's website.
Image 1:
This image contains text that lists specifications for two different car models, one with Rear-Wheel Drive and the other with Long Range AWD (All-Wheel Drive). Categories covered include Battery, Weight, Acceleration, Range, Top Speed, Drive, Seating, Wheels, and Warranty.
Image 2:
This image shows a cutaway illustration of an electric vehicle highlighting its structural components. The car is rendered to show its internal features such as rigid structure and impact protection zones.
Image 3:
Similar to the first image, this image contains text showing specifications for two variants of what appears to be the same model of electric vehicle, with one being a performance model and the other Long Range AWD. The specs include Battery, Acceleration, Range, Drive, Seating, Wheels, Display, Tire Type, Supercharging Max/Power, and Warranty.
Image 4:
The image presents pricing and potential savings information for different variants of an electric vehicle model. It includes a federal incentive notice, an area to enter a delivery postal code, purchase price for different versions (Model Y Rear-Wheel Drive, Model Y Long Range, Model Y Performance), and additional feature details. There's also a note about potential savings over gas at the bottom.
Image 5:
This image lists specifications for electric vehicles, focused on two categories: Performance and Long Range AWD. Specs listed include Battery, Acceleration, Range, Top Speed, Drive, Seating, Wheels, Display, Tire Type, Supercharging Max/Power, and Warranty.
Each of these images would be used to provide customers with information regarding electric car models, their features, capabilities, pricing, and potential savings.
response_2 = openai_mm_llm.complete(
prompt="Can you tell me what is the price with each spec?",
image_documents=image_documents,
)
print(response_2)
The images you've provided appear to be from a car manufacturer's website, showing different specifications for an electric vehicle and the associated prices for different trim levels or configurations of the vehicle. However, since the actual text content for the price per specification is not fully legible in the images provided, I can't give you precise pricing information. Generally, these types of websites often list the following trims with increasing features and therefore increasing prices:
1. Rear-Wheel Drive (Standard Range or Long Range)
2. Dual Motor All-Wheel Drive (often dubbed Long Range AWD)
3. Performance (typically comes with the most features and fastest acceleration)
Features like acceleration times, range, top speed, curb weight, cargo volume, seating capacity, display type, drive type, wheels size, warranty, and others can vary by trim level. The images show that there are different specs for the "Performance" and "Long Range AWD" trims such as acceleration, range, top speed, and potentially others related to power and luxury features.
The final image provided shows some pricing details:
- Model 3 Rear-Wheel Drive: $57,990
- Model 3 Dual Motor All-Wheel Drive: $67,990
- Model 3 Performance: $74,990
These prices might be eligible for certain incentives, as indicated by a "$5,000 Federal Incentive" notice, which would effectively reduce the purchase price, though this depends on individual eligibility and local laws.
Please proactively check the manufacturer’s website or reach out to an official dealership for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding pricing and specifications for these vehicle trims.
Generating text, pdf, images data from raw files [Wikipedia, SEC files] for Multi Modal Index/Retrieval#
import requests
def get_wikipedia_images(title):
response = requests.get(
"https://en.wikipedia.org/w/api.php",
params={
"action": "query",
"format": "json",
"titles": title,
"prop": "imageinfo",
"iiprop": "url|dimensions|mime",
"generator": "images",
"gimlimit": "50",
},
).json()
image_urls = []
for page in response["query"]["pages"].values():
if page["imageinfo"][0]["url"].endswith(".jpg") or page["imageinfo"][
0
]["url"].endswith(".png"):
image_urls.append(page["imageinfo"][0]["url"])
return image_urls
from pathlib import Path
import requests
import urllib.request
image_uuid = 0
# image_metadata_dict stores images metadata including image uuid, filename and path
image_metadata_dict = {}
MAX_IMAGES_PER_WIKI = 20
wiki_titles = {
"Tesla Model Y",
"Tesla Model X",
"Tesla Model 3",
"Tesla Model S",
"Kia EV6",
"BMW i3",
"Audi e-tron",
"Ford Mustang",
"Porsche Taycan",
"Rivian",
"Polestar",
}
data_path = Path("mixed_wiki")
if not data_path.exists():
Path.mkdir(data_path)
for title in wiki_titles:
response = requests.get(
"https://en.wikipedia.org/w/api.php",
params={
"action": "query",
"format": "json",
"titles": title,
"prop": "extracts",
"explaintext": True,
},
).json()
page = next(iter(response["query"]["pages"].values()))
wiki_text = page["extract"]
with open(data_path / f"{title}.txt", "w") as fp:
fp.write(wiki_text)
images_per_wiki = 0
try:
# page_py = wikipedia.page(title)
list_img_urls = get_wikipedia_images(title)
# print(list_img_urls)
for url in list_img_urls:
if (
url.endswith(".jpg")
or url.endswith(".png")
or url.endswith(".svg")
):
image_uuid += 1
# image_file_name = title + "_" + url.split("/")[-1]
urllib.request.urlretrieve(
url, data_path / f"{image_uuid}.jpg"
)
images_per_wiki += 1
# Limit the number of images downloaded per wiki page to 15
if images_per_wiki > MAX_IMAGES_PER_WIKI:
break
except:
print(str(Exception("No images found for Wikipedia page: ")) + title)
continue
!wget "https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/mlaymdy1ni1ovyeykhhuk/tesla_2021_10k.htm?rlkey=qf9k4zn0ejrbm716j0gg7r802&dl=1" -O ./mixed_wiki/tesla_2021_10k.htm
Build Multi-modal index and vector store to index both text and images#
from llama_index.indices.multi_modal.base import MultiModalVectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.vector_stores import QdrantVectorStore
from llama_index import SimpleDirectoryReader, StorageContext
import qdrant_client
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
)
# Create a local Qdrant vector store
client = qdrant_client.QdrantClient(path="qdrant_mm_db")
text_store = QdrantVectorStore(
client=client, collection_name="text_collection"
)
image_store = QdrantVectorStore(
client=client, collection_name="image_collection"
)
storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(
vector_store=text_store, image_store=image_store
)
# Create the MultiModal index
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./mixed_wiki/").load_data()
index = MultiModalVectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
storage_context=storage_context,
)
# Save it
# index.storage_context.persist(persist_dir="./storage")
# # Load it
# from llama_index import load_index_from_storage
# storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(
# vector_store=text_store, persist_dir="./storage"
# )
# index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context, image_store=image_store)
print(response_2.text)
Retrieve and query texts and images from our Multi-Modal Index#
We show two examples leveraging multi-modal retrieval.
Retrieval-Augmented Captioning: In the first example, we perform multi-modal retrieval based on an existing image caption, to return more relevant context. We can then continue to query the LLM for related vehicles.
Multi-modal RAG Querying: In the second example, given a user-query, we first retrieve a mix of both text and images, and feed it to an LLM for synthesis.
1. Retrieval-Augmented Captioning#
# generate Text retrieval results
MAX_TOKENS = 50
retriever_engine = index.as_retriever(
similarity_top_k=3, image_similarity_top_k=3
)
# retrieve more information from the GPT4V response
retrieval_results = retriever_engine.retrieve(response_2.text[:MAX_TOKENS])
from llama_index.response.notebook_utils import display_source_node
from llama_index.schema import ImageNode
retrieved_image = []
for res_node in retrieval_results:
if isinstance(res_node.node, ImageNode):
retrieved_image.append(res_node.node.metadata["file_path"])
else:
display_source_node(res_node, source_length=200)
plot_images(retrieved_image)
Node ID: 8a67ab30-545c-46ee-a25f-64c95a4571be
Similarity: 0.7758026357212682
Text: == Reception ==
Consumer Reports wrote that the all-wheel-drive Model X 90D largely disappoints, as rear doors are prone to pausing and stopping, the second-row seats that cannot be folded, and the…
Node ID: 5db1e928-197d-41d4-b1c1-34d2bcf1cc4d
Similarity: 0.7712850768830459
Text: == Design and technology ==
=== Body and chassis ===
The i3 was the first mass production car with most of its internal structure and body made of carbon-fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP). BMW took…
Node ID: 89e533c6-3e25-4933-b58a-7d42ac67e957
Similarity: 0.768609543932987
Text: === Autoshift ===
Introduced in mid-2021, the Plaid and Long Range versions of the Model S feature no steering column-mounted shift stalk; instead, the Model S uses cameras to infer whether to shif…

response_3 = openai_mm_llm.complete(
prompt="what are other similar cars?",
image_documents=image_documents,
)
print(response_3)
The images provided show information about electric vehicles, specifically the Model Y. This is a compact crossover SUV from a prominent electric vehicle manufacturer. When considering similar vehicles in the electric automobile market, you might want to look at the following models that offer comparable characteristics, in terms of performance, size, and luxury:
1. Tesla Model 3 - A smaller sedan from the same manufacturer with similar technology and performance capabilities.
2. Chevrolet Bolt EUV - A compact electric SUV with semi-autonomous driving capabilities.
3. Ford Mustang Mach-E - An all-electric SUV that offers performance and technology options.
4. Volkswagen ID.4 - An electric SUV with a focus on interior space and comfort.
5. Hyundai Kona Electric - A compact electric SUV with a competitive range and features.
6. Kia EV6 - An electric crossover with a sporty design and good performance metrics.
7. Audi Q4 e-tron - A luxury compact electric SUV with a focus on performance and high-end features.
8. Volvo XC40 Recharge - An electric version of Volvo's popular compact SUV with an emphasis on safety and Scandinavian design.
Each of these vehicles offers a different mix of range, performance, interior space, technology, and price. When comparing them to the Model Y specifications seen in the images, factors such as acceleration, range, weight, cargo volume, and top speed can be used to evaluate their similarities and differences. Keep in mind that new electric vehicle models are continuously being released, so it's always good to check the latest offerings for the most current comparisons.
2. Multi-Modal RAG Querying#
from llama_index.prompts import PromptTemplate
from llama_index.query_engine import SimpleMultiModalQueryEngine
qa_tmpl_str = (
"Context information is below.\n"
"---------------------\n"
"{context_str}\n"
"---------------------\n"
"Given the context information and not prior knowledge, "
"answer the query.\n"
"Query: {query_str}\n"
"Answer: "
)
qa_tmpl = PromptTemplate(qa_tmpl_str)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(
multi_modal_llm=openai_mm_llm, text_qa_template=qa_tmpl
)
query_str = "Tell me more about the Porsche"
response = query_engine.query(query_str)
print(str(response))
The Porsche Taycan represents a significant step for Porsche as their first series production electric car. The Taycan model line includes a diverse range of variants: from the more affordable base rear-wheel-drive (RWD) model to the high-performance all-wheel-drive (AWD) Turbo and Turbo S models. The Taycan is not limited to just the 4-door saloon format but has expanded to include estate variations such as the Taycan Cross Turismo and the Taycan Sport Turismo.
The interior of the Taycan is a showcase of Porsche's commitment to modernity and technology, with up to four digital displays for instrumentation and infotainment, while still retaining iconic features like the classic Porsche clock. The exterior design is a tribute to Porsche's heritage with contemporary touches, maintaining the brand's visual language.
Performance-wise, the Taycan offers different power options, with the most powerful Turbo and Turbo S variants reaching 460 kW (617 hp) under specific conditions like overboost power with launch control mode. The Taycan's design incorporates advanced features like a retractable rear spoiler and door handles, and it utilizes a regenerative braking system to optimize efficiency.
The Taycan has not only impressed customers and the automotive market but has also earned accolades from prestigious entities, with the 4S model being named Performance Car of the Year by What Car? magazine, and the Taycan Cross Turismo gaining recognition as Best Estate in the Top Gear Electric Awards.
Moreover, the concept cars that previewed the Taycan, specifically the Porsche Mission E and the Mission E Cross Turismo, pointed toward Porsche's electric future and set a benchmark in the electric vehicle market for design and performance expectations. The Mission E concept set ambitious goals for range and charging time, leveraging an 800 V DC system voltage for rapid charging capabilities.
Overall, the Porsche Taycan is a blend of traditional Porsche DNA and forward-looking electric vehicle technology, epitomizing high performance, luxury, and sustainability in a package that appeals to both loyal customers and a new generation seeking electric alternatives.
# show sources
from llama_index.response.notebook_utils import display_source_node
for text_node in response.metadata["text_nodes"]:
display_source_node(text_node, source_length=200)
plot_images(
[n.metadata["file_path"] for n in response.metadata["image_nodes"]]
)
Node ID: c9dac736-51ce-429a-9b77-96c95a00d91f
Similarity: 0.8241315758378377
Text: == Models ==
The Taycan is currently offered as a 4-door saloon model and a 4-door estate model, the Taycan Cross Turismo. Other planned variants include a two-door coupe and convertible models, wh…
Node ID: 531c87f5-fcc4-453e-a013-fa6c9a3a7d24
Similarity: 0.822575963523647
Text: The Porsche Taycan is a battery electric saloon and shooting brake produced by German automobile manufacturer Porsche. The concept version of the Taycan, named the Porsche Mission E, debuted at the…
